Launch of AP-Swiss, the IAP Ambassador Platform for Switzerland

ESA's Integrated Applications Promotion (IAP) programme has partnered with the Swiss Space Office to establish an Ambassador Platform dedicated to fostering the development of integrated space-based applications with and for the Swiss industry: AP-Swiss.
About IAP
The IAP programme supports the development and validation of viable operational services relying on a combination of space systems (Telecommunication, Navigation, Earth Observation, Manned Space Technologies). By using and integrating these systems with non-space assets, improved and new services on a regional, national or global scale can be created for a wide range of users.
The role of AP-Swiss
As with all IAP Ambassador Platforms, the role of the IAP Swiss Platform is to:
-
Increase awareness amongst economic actors about the potential added-value of space technologies;
-
Stimulate the emergence of new ideas and services;
-
Help create international partnerships so as to generate a global customer base needed for services to be sustainable;
-
Be an "honest broker" between ESA and Swiss stakeholders (e.g., "spacetech" companies, solution/service providers, customers, user communities).
AP-Swiss helps companies to target new services, identify Swiss, European and international partners and obtain funding from ESA for awareness, feasibility and demonstration activities, up to market validation.
Such a partnership brokering is critical to develop truly integrated applications, combining multiple space and non-space systems to deliver complete solutions and reach wider markets.
AP-Swiss will have a definite Swiss focus. Its remit includes the many multinational companies and organisations that are based in the country and whose activities are global. Its focus will be on food security, water management, transport logistics and safety, renewable energy, banking and insurance, aid and health for developing countries and regional development.
About AP-Swiss
The IAP Ambassador Platform for Switzerland is managed by José Achache, previously Executive Director of the Group on Earth Observations in Geneva, Deputy Director General for Research and Technology at CNES, and a former Director of Earth Observation Programmes at ESA. In addition to numerous scientific publications, Professor Achache is the author of "Les Sentinelles de la Terre", an essay on space policy, space technologies and their applications.
AP-Swiss is located in the Innovation Square of the EPFL Science Park in Lausanne. This hands-on incubator was established to support innovative technology companies and projects in their early years, taking science to market. With approximately 100 start-up companies, the "innovation cells" of many large corporations and the proximity to the Swiss Space Center, the Science Park provides the perfect eco-system for AP-Swiss to mature new and innovative applications of space-based infrastructures, in close cooperation with all stakeholders in Switzerland.



 The Satellite-enhanced eHealth for sub-Saharan Africa (eHSA) Programme intends to deliver economically sustainable eHealth services in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA). The programme.s to federate stakeholders from various organizations along the service provision chain will shape its success. This portal serves as a tool facilitating exchange of news, contacts and discussion among the stakeholders.
The Satellite-enhanced eHealth for sub-Saharan Africa (eHSA) Programme intends to deliver economically sustainable eHealth services in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA). The programme.s to federate stakeholders from various organizations along the service provision chain will shape its success. This portal serves as a tool facilitating exchange of news, contacts and discussion among the stakeholders.

 The
The  The
The  A one-shop-stop solution for affordable access to satellite services is one step closer to the marketplace, thanks to a little ingenuity from industry and ESA.s
A one-shop-stop solution for affordable access to satellite services is one step closer to the marketplace, thanks to a little ingenuity from industry and ESA.s  The Integrated Applications Promotion programme (IAP) in the Directorate of Telecommunications and Integrated Applications is now re-advertising a vacancy for an Internal Research Fellowship with a starting date in Autumn 2012. The Research Fellowship will be based at Harwell in the UK. The focus of the fellowship is on applications development; as such it is relevant for applicants from a wide range of academic backgrounds, which may include economics, business studies, commerce, geography, ITC, or a specific industry sector with a potential need for space-based services. Expertise in space science and technology, whilst preferred, is not a pre-requisite.
The Integrated Applications Promotion programme (IAP) in the Directorate of Telecommunications and Integrated Applications is now re-advertising a vacancy for an Internal Research Fellowship with a starting date in Autumn 2012. The Research Fellowship will be based at Harwell in the UK. The focus of the fellowship is on applications development; as such it is relevant for applicants from a wide range of academic backgrounds, which may include economics, business studies, commerce, geography, ITC, or a specific industry sector with a potential need for space-based services. Expertise in space science and technology, whilst preferred, is not a pre-requisite. Details on the Demonstration of
Details on the Demonstration of 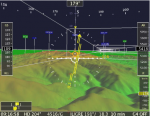 Small and mid-sized airports face many challenges. Airport traffic is unevenly distributed over the day; general aviation traffic directed to minor airports cannot usually rely on the availability of flight information services, and in many cases general aviation aircraft flying inside non controlled airspaces cannot rely on air traffic controllers ensuring separation against other aircraft.
Small and mid-sized airports face many challenges. Airport traffic is unevenly distributed over the day; general aviation traffic directed to minor airports cannot usually rely on the availability of flight information services, and in many cases general aviation aircraft flying inside non controlled airspaces cannot rely on air traffic controllers ensuring separation against other aircraft. Another issue faced by small airports is the production Aerodrome Obstacle Charts. This must be done periodically to ensure the required level of safety ANSPs (Air Navigation Service Providers). Currently this is done by the use of expensive aero photogrammetric techniques and on-site surveys by traditional topographic techniques.
Another issue faced by small airports is the production Aerodrome Obstacle Charts. This must be done periodically to ensure the required level of safety ANSPs (Air Navigation Service Providers). Currently this is done by the use of expensive aero photogrammetric techniques and on-site surveys by traditional topographic techniques. Together with the Swiss Space Office, the European Space Agencyâs Integrated Applications Promotion (IAP) programme wishes to announce a vacancy for a Swiss ESA IAP Ambassador Platform manager. This manager will be responsible for the Swiss IAP Ambassador Platform (AP), and will start their duties on 1st October 2012.
Together with the Swiss Space Office, the European Space Agencyâs Integrated Applications Promotion (IAP) programme wishes to announce a vacancy for a Swiss ESA IAP Ambassador Platform manager. This manager will be responsible for the Swiss IAP Ambassador Platform (AP), and will start their duties on 1st October 2012.